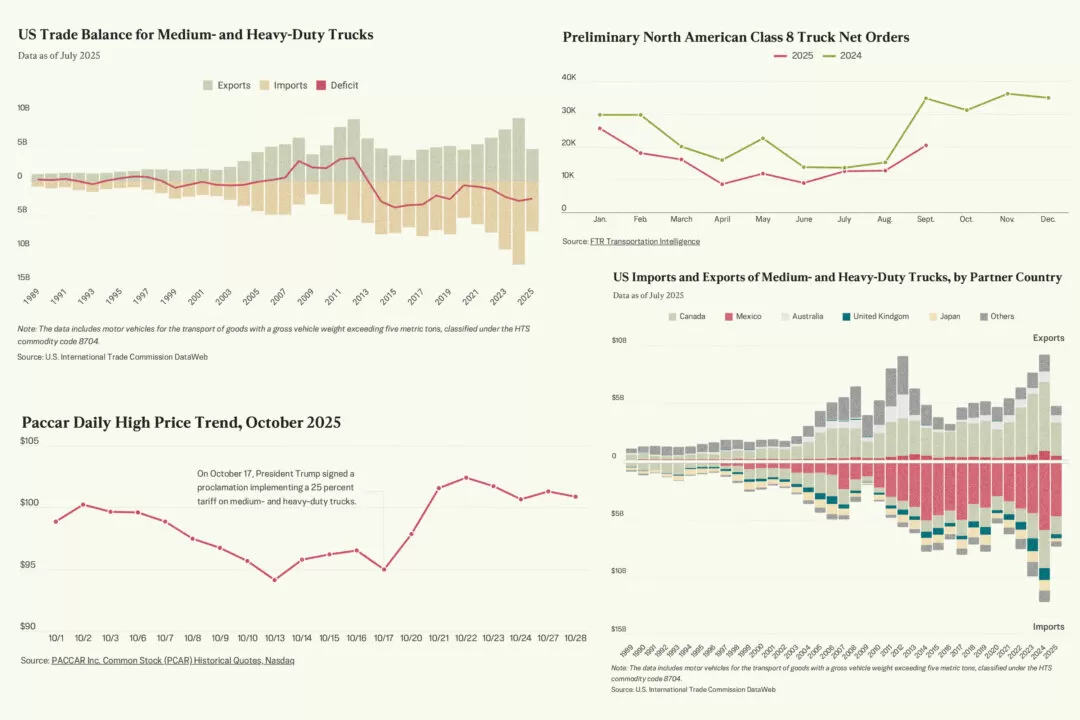
The U.S. trade deficit with Mexico has been a topic of concern for many years, and recent reports have shown that it continues to grow. In 2024, the trade deficit for medium- and heavy-duty trucks between the two countries reached a staggering $5.1 billion. This is a significant increase from the previous year and highlights the need for action to address this issue.
The trade deficit refers to the difference between the value of goods and services that a country imports and the value of goods and services that it exports. In the case of the U.S. and Mexico, the trade deficit for medium- and heavy-duty trucks means that the U.S. is importing more of these vehicles from Mexico than it is exporting to them. This has a direct impact on the U.S. economy and the trucking industry.
One of the main reasons for this trade deficit is the difference in labor costs between the two countries. Mexico has lower labor costs, making it more attractive for U.S. companies to manufacture their trucks there. This, in turn, leads to a decrease in the production of trucks in the U.S. and an increase in imports from Mexico. This trend has been ongoing for several years and has now reached a critical point.
The impact of this trade deficit on the U.S. economy cannot be ignored. It not only affects the trucking industry but also has a ripple effect on other related industries. The decrease in truck production in the U.S. means a loss of jobs and revenue for American workers and companies. It also puts a strain on the U.S. economy as a whole, as the country is spending more money on imports than it is earning from exports.
Furthermore, the trade deficit with Mexico also has implications for national security. The U.S. relies heavily on the trucking industry to transport goods and materials across the country. With a significant portion of these trucks being imported from Mexico, it raises concerns about the country’s dependence on foreign sources for essential goods. In times of crisis, this could prove to be a significant vulnerability for the U.S.
However, it is not all doom and gloom. The trade deficit with Mexico also presents an opportunity for the U.S. to address the issue and work towards a more balanced trade relationship. This can be achieved through various measures, such as implementing policies to incentivize truck production in the U.S. and reducing the cost of production. This would not only decrease the trade deficit but also create more jobs and boost the economy.
Another solution could be to negotiate a new trade agreement with Mexico that addresses the trade deficit and promotes fair trade practices. The United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), which replaced the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), could be a step in the right direction. The USMCA includes provisions to increase the production of trucks in the U.S. and reduce the trade deficit with Mexico.
Moreover, the U.S. could also focus on increasing exports of medium- and heavy-duty trucks to other countries. This would not only decrease the trade deficit with Mexico but also diversify the market for American truck manufacturers. It would also help in reducing the country’s dependence on a single trading partner.
In conclusion, the U.S. trade deficit with Mexico for medium- and heavy-duty trucks reaching $5.1 billion in 2024 is a cause for concern. It highlights the need for action to address this issue and work towards a more balanced trade relationship. While the trade deficit has its challenges, it also presents an opportunity for the U.S. to implement measures that would benefit the economy and the trucking industry. With the right policies and agreements in place, the U.S. can reduce the trade deficit and create a more sustainable and mutually beneficial trade relationship with Mexico.