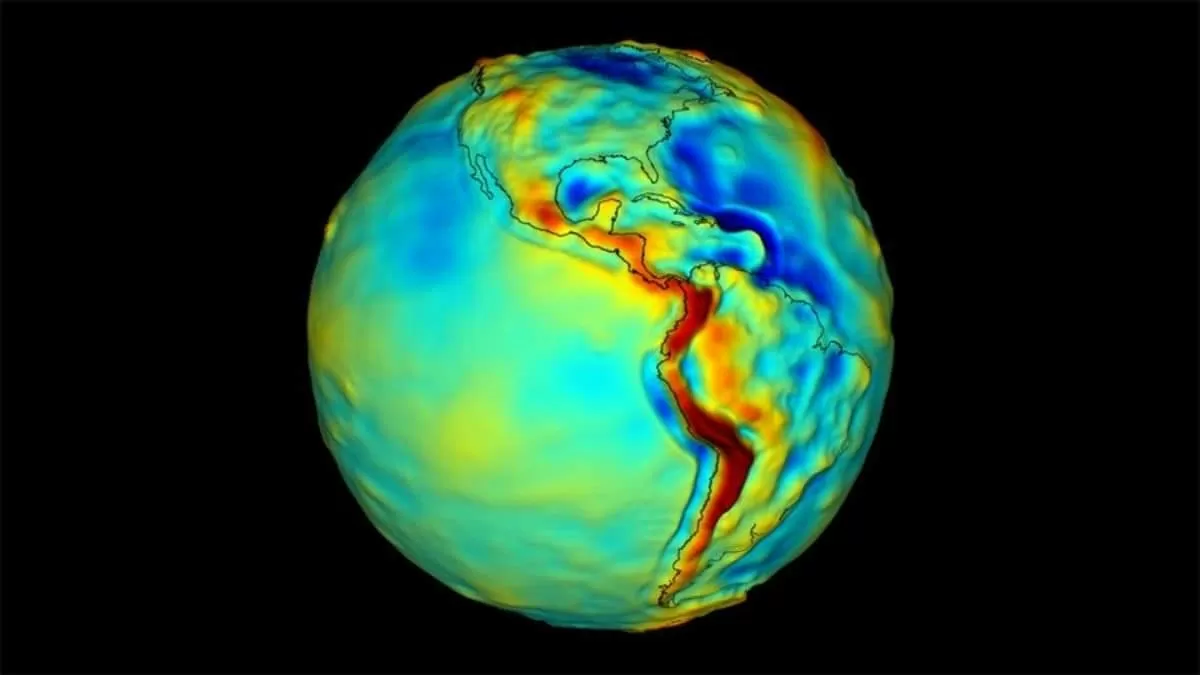
NASA, in collaboration with academia and private companies, is embarking on an exciting new mission that could revolutionize our understanding of Earth’s subsurface and pave the way for future exploration of other planetary bodies in our solar system. This groundbreaking project involves the development of the first quantum sensor to map Earth’s gravity from space, using cold rubidium atoms to deliver highly sensitive and long-term measurements.
The idea of using quantum technology to study Earth’s gravity is not a new one, but it has never been attempted on this scale before. With the help of leading experts from various fields, including scientists from academia and industry, NASA is pushing the boundaries of what is possible and taking a giant leap towards unlocking the secrets of our planet.
The concept of a quantum sensor may sound complex, but the basic principle is quite simple. By using ultra-cold rubidium atoms, which are cooled to just a fraction of a degree above absolute zero, scientists can create a highly sensitive instrument that is capable of measuring even the tiniest changes in Earth’s gravitational field. This is a significant improvement over traditional sensors, which are limited by the effects of temperature and other external factors.
One of the most exciting aspects of this mission is its potential to transform our understanding of Earth’s subsurface. By mapping the planet’s gravity in unprecedented detail, scientists will be able to create a 3D image of what lies beneath the surface. This will not only provide valuable insights into the structure and composition of our planet, but it could also help us better understand geological processes such as earthquakes, volcanoes, and plate tectonics.
But the benefits of this mission go beyond Earth. The data collected by the quantum sensor could also be used to study other planetary bodies in our solar system, such as Mars and the Moon. By measuring their gravity, we can gain a better understanding of their internal structure and composition, which is crucial for future exploration and potential colonization.
The potential applications of this technology are endless. It could be used to detect underground water sources, locate mineral deposits, and even aid in the search for extraterrestrial life. This mission has the power to transform the way we explore and understand not just our own planet, but the entire universe.
The development of this quantum sensor is a collaborative effort between NASA, academia, and private companies. This partnership is crucial in pushing the boundaries of science and technology and bringing this ambitious project to fruition. It also highlights the importance of collaboration and knowledge-sharing in advancing our understanding of the world around us.
The compact size of the instrument is also worth noting. Traditional gravity sensors used for space missions are large and bulky, making them difficult and expensive to launch into orbit. However, the quantum sensor being developed by NASA is compact and lightweight, making it easier and more cost-effective to send into space. This opens up new possibilities for future missions and could lead to more frequent and widespread use of this technology.
The potential impact of this mission cannot be overstated. By providing highly sensitive and long-term measurements of Earth’s gravity, the quantum sensor has the potential to transform our understanding of our planet and pave the way for future exploration of other worlds. It is a testament to the ingenuity and determination of the human spirit and a reminder of what we can achieve when we work together towards a common goal.
In conclusion, NASA’s collaboration with academia and private companies to develop the first quantum sensor to map Earth’s gravity from space is a groundbreaking mission that has the potential to transform our understanding of our planet and beyond. With its compact size, high sensitivity, and long-term measurement capabilities, this instrument has the power to revolutionize how we study Earth’s subsurface and explore other planetary bodies in our solar system. It is a testament to the endless possibilities of science and technology and a reminder that the sky is not the limit for human exploration and discovery.