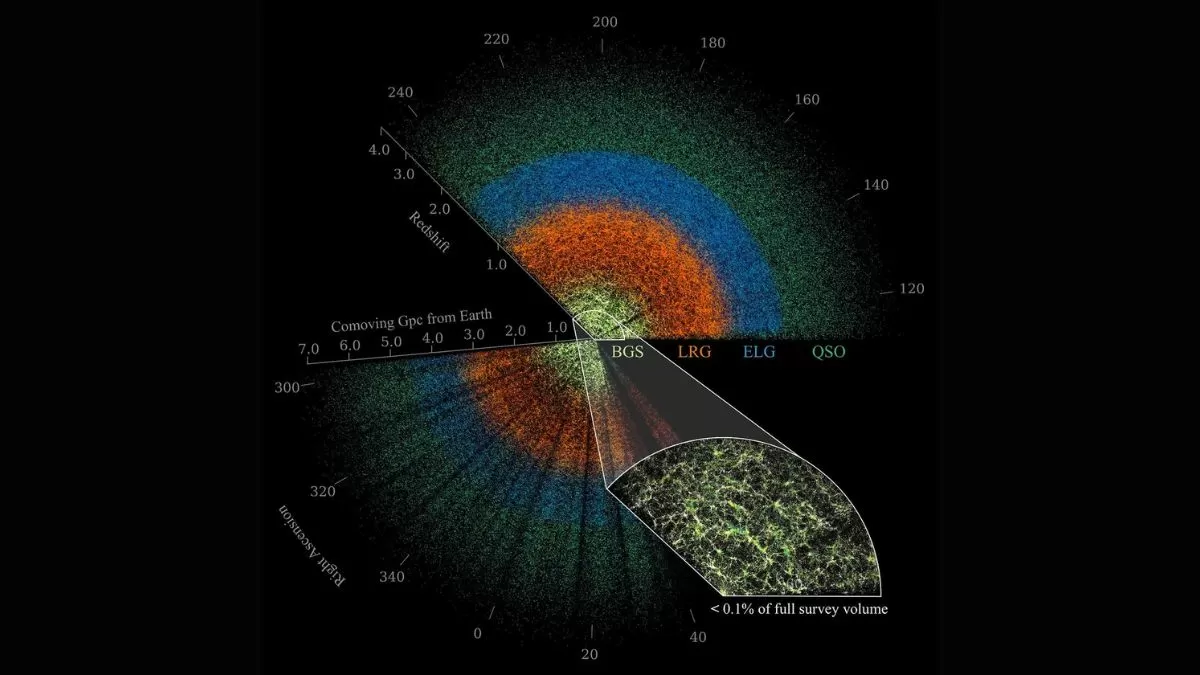
New research from the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) project has shed new light on the mysterious force known as dark energy. This groundbreaking study, which involved mapping 15 million galaxies, has challenged long-held cosmological models and raised new questions about the evolution of our universe.
For years, dark energy has been a topic of fascination and confusion for scientists. It was first proposed in the late 1990s to explain the accelerating expansion of the universe. This force is thought to make up around 70% of the total energy in the universe, yet its nature and behavior have remained elusive.
One of the biggest assumptions about dark energy has been that it is a constant force, with a consistent influence on the expansion of the universe. However, the latest findings from DESI suggest that this may not be the case. The project’s data has revealed that dark energy may actually be changing over time, challenging the long-held belief that it is a stable force.
DESI’s findings have been made possible through an incredibly detailed map of the universe. By measuring the light from 15 million galaxies, scientists were able to create a 3D map of their locations and movements. This map has provided a deeper understanding of the universe’s expansion and has allowed researchers to study the effects of dark energy in more detail.
The results of this study have raised new questions about the evolution of our universe. If dark energy is not a constant force, then it may have played a different role in the early stages of the universe’s expansion than it does now. This challenges the traditional understanding of cosmic evolution and may require scientists to rethink their theories.
One of the most exciting aspects of this research is that it opens up new avenues for exploration. Scientists are now eager to dive deeper into the data provided by DESI and continue to unravel the mysteries of dark energy. This new understanding may also lead to the development of new models and theories about the evolution of the universe.
The DESI project has been a massive undertaking, involving the collaboration of over 500 scientists from around the world. This international effort has been crucial in collecting and analyzing the vast amounts of data needed to map 15 million galaxies. The success of this project is a testament to the dedication and hard work of the scientific community.
The implications of DESI’s findings go beyond the world of astrophysics. This research has the potential to impact our understanding of the fundamental laws of physics and may even lead to new discoveries and breakthroughs in other fields. It is a reminder of the interconnectedness of all sciences and the importance of pushing the boundaries of our knowledge.
The DESI project is a prime example of the power of collaboration and the importance of investing in scientific research. It is through projects like these that we are able to make significant advancements in our understanding of the universe and our place within it. The findings of this study will undoubtedly inspire and motivate future generations of scientists to continue the pursuit of knowledge.
In conclusion, the latest findings from the DESI project have challenged our long-held beliefs about dark energy and its role in the evolution of the universe. By mapping 15 million galaxies, scientists have uncovered evidence that this force may be changing over time, raising new questions and sparking further research. This is a significant step forward in our understanding of the cosmos and a reminder of the endless possibilities that await us in the vast expanse of space.